باز آفرینی علم و هنر Dentistry & Medicine
علم امروز و هنر دیروزباز آفرینی علم و هنر Dentistry & Medicine
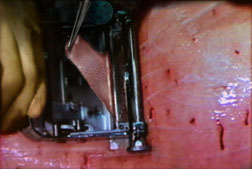
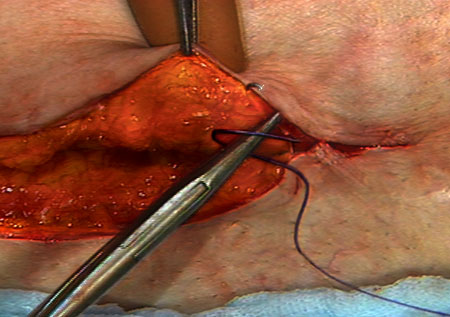
علم امروز و هنر دیروزانواع بخیه
این نوع بخیه تحت نام بخیه ممتد یا همان continuous هم در بخش بالینی ما شناخته شده است شکل کاملا واضح است اما اگر باز هم مشکلی بود پیغام بگذارید تا توضیح کامل فارسی بگذارم.
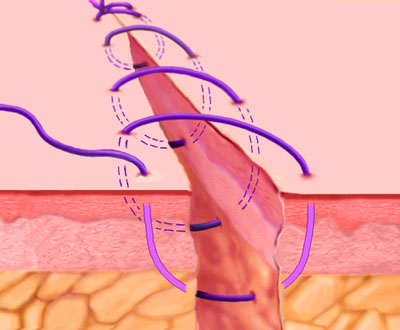
Running, or Continuous Stitch
The "Running" stitch is made with one continuous length of suture material. Used to close tissue layers which require close approximation, such as the peritoneum. May also be used in skin or blood vessels. The advantages of the running stitch are speed of execution, and accommodation of edema during the wound healing process. However, there is a greater potential for malapproximation of wound edges with the running stitch than with the interrupted stitch
بخیه ای که در کشور ما با نام ساده یا simple شناخته شده است.
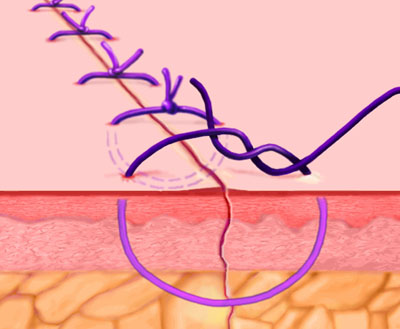
Interrupted Stitch
Each stitch is tied separately. May be used in skin or underlying tissue layers. More exact approximation of wound edges can be achieved with this technique than with the running stitch
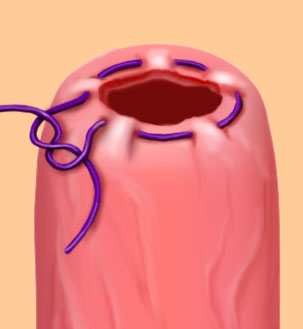
Purse String
A continuous stitch paralleling the edges of a circular wound. The wound edges are inverted when tied. Commonly used to close circular wounds, such as hernia or an appendiceal stump
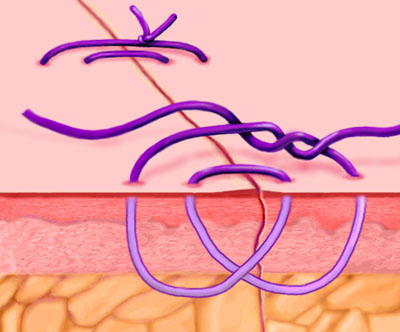
Smead-Jones/Far-and-Near
A double loop technique alternating far and near stitches, and possessing greater mechanical strength than continuous or simple interrupted sutures. Commonly used for approximating fascial edges, especially for patients at risk for fascial disruption or infection
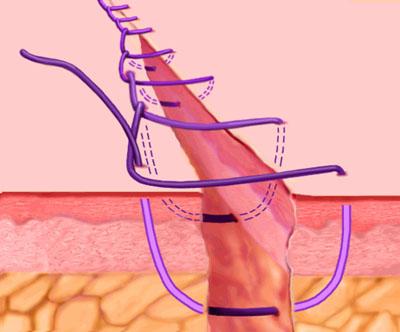
Continuous Locking, or Blanket Stitch
A self-locking running stitch used primarily for approximating skin edges
انواع نخ ها
Polypropylene: a nonabsorbable, monofilament material that is the least reactive of all suture materials; it is used with continuous percutaneous suturing. Its disadvantage is that it has coiled memory, making it difficult to handle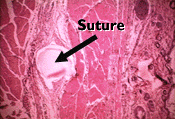
Nylon: a nonabsorbable suturing material that degrades in vivo by hydrolysis at a rate of about 125% annually. The advantages of nylon are good pliability and ease of handling. It is favored for interrupted percutaneous suture closures. Nylon sutures are available in monofilament and multifilament construction. Braided nylon sutures possess the same handling and knot construction characteristics as silk sutures, but unlike natural fiber, nylon is relatively nonreactive in tissue
Synthetic absorbable: absorbable refers to the degradation and loss of tensile strength within 60 days. Absorption and loss of tensile strength are not interchangeable. The former is important only with regard to late suture complications; the latter speaks to the primary function of the suture -- maintaining tissue approximation
Braided synthetic absorbable: useful for interrupted dermal suture and ligating bleeders
Monofilament synthetic absorbable: indicated for continuous dermal suture
تصاویر و تکنیک های قشنگی است ببینید!
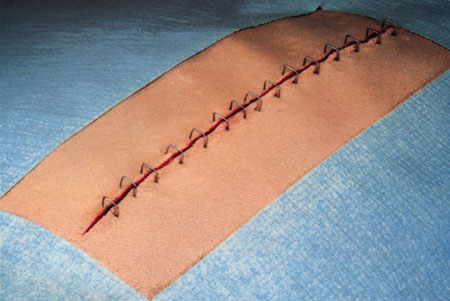
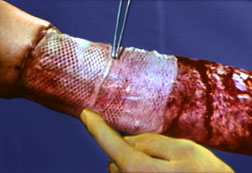
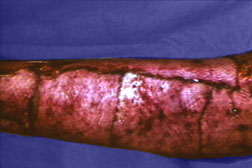
Staples
Staples are less reactive than the least reactive suture. Deeply implanted staples do not affect tissue defenses, although staple cross members that are flush with the skin can produce cross-hatched scarring. The development of disposable staplers with absorbable tacks obviates the need for removal of staples. Subcuticular closure of skin is now also possible through the use of a disposable stapler that uses twin gripper blades to approximate and evert the wound edges and insert a disposable pin into the dermis
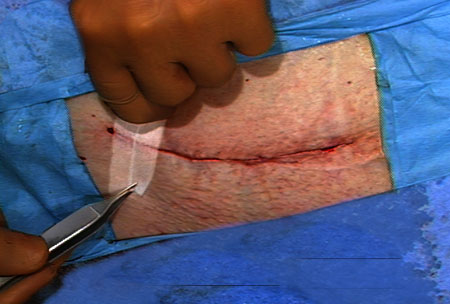
Tape is the least reactive of man-made wound closure materials. Tape with hypoallergenic adhesive on spun bonded nylon without reinforcing filaments has the best record for avoiding premature detachment. It also reduces the incidence of stress blister formation
|
|
Types of Wound Closure: |
|
| |
|
|
Orthodontics for Adults ارتودنسی بزرگسالان
1. Is it unusual for adults to have orthodontic treatment- More and more adults are having orthodontic treatment to correct crooked or crowded teeth
- Orthodontics can make the teeth more attractive and more functional, by improving jaw alignment, and correcting "the bite"
- Improved techniques have been devised for treating adults
- Modern orthodontic braces are less obtrusive and adults are more willing to wear them
2. Is adult orthodontic treatment successful
- Adult orthodontics is particularly successful for correcting crowding and jaw problems
- Healthy teeth can be moved with braces at any age
- Very similar treatments and appliances are used for children and adults
 Before Before |
 after after |
3. I've always had crooked teeth. Does it really matter
- Crooked teeth can prevent you from chewing properly, and lead to jaw joint problems
- Improving "the bite" can make eating more efficient and comfortable
- Crooked teeth affect your appearance and most people want to look their best at any age
- People with unattractive teeth are often too embarrassed to smile. Orthodontic treatment enables you to smile with confidence
- Looking better can make you feel better about yourself, and can increase your self-confidence
4. What are the most common orthodontic treatments for adults
- Correcting crowding or crooked teeth
 Crowding
Crowding - Closing newly developed or old spaces between teeth

Before Treatment
Treatment After
After - Correcting the position and alignment of teeth
Teeth often tilt into gaps left by extractions. These teeth have to be moved into a more upright position
This correction makes it possible to use replacement crowns, implants, fixed bridges, or removable partial dentures to replace the missing teeth - The photographs below explain what can be done for an adult, when the orthodontist, periodontist and prosthodontist all work together
 Before |
 Upper crowns Upper crownsLower brace |
 Lower teeth Lower teethstraightened | ||
 Final result | ||||
5. What problems could make orthodontic treatment for adults more difficult
- Periodontal Disease
- Adults may suffer from periodontal disease, which is a deterioration of the gums and underlying bone
- Periodontal treatment will be necessary before the orthodontic treatment can start
- Tooth decay
- All dental decay should be treated before orthodontic treatment starts
- It is less comfortable to have dental treatment after braces have been fitted
- Abnormal jaw relationships
- The growth of the jaws has been completed in adults, and so this treatment is not always possible
- In children, the ongoing growth of the jaw can be directed to correct the abnormalities that are present
 Lower jaw
Lower jaw
protrusion Lower jaw
Lower jaw
protrusion - Worn down or broken teeth
- These must be built up or restored before orthodontic treatment can start
- Lack of commitment
- Adult patients may find it hard to commit to long term treatment, especially to wearing braces for long periods
6. Can an orthodontist help my painful jaw muscles and joints
- Your orthodontist or dentist will be able to diagnose the problem
- This problem can be caused by the grinding and clenching of teeth
- The action is unconscious and involuntary
- The technical name for it is "bruxism"
- Bruxism usually happens during sleep
- It wears down the teeth, and causes stress and trauma to the jaw muscles and the teeth
- The orthodontist will probably suggest a splint, bite plate or a nightguard to protect the teeth during sleep. This will also relax the muscles of the jaw
- These devices should relieve and prevent the results of tooth grinding
- The cause of the bruxism may be psychological, and may have to be treated by a suitable therapist
 Nightguard Nightguard |
 Nightguard in place Nightguard in place |
Periapical pathosis

Description: Well-delineated ovoid-shaped radiolucency at the apex of the lateral incisor.
Location: Periapical area of maxillary lateral incisor
هماتوم ساب دورال حاد
Acute Subdural Hematoma
 |
| Subacute subdural hematoma |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
acute sinusitis
عکسی شماتیک و زیبا از سینوزیت حاد
| توصیف بیماری | |||
|
| نشانه ها |
|
| عوامل مسبب |
|
| تشخیص ما چگونه باشد؟ |
|
| درمان |
|
| شرایط مساوی(similar condition) |
|
| متفرقه و گوناگونll |
|

 سالم(شکل بیماری در پایین همین صفحه)
سالم(شکل بیماری در پایین همین صفحه)